how to grow tomatoes from seeds in a pot – [Beginners Guide]
Hello there! Are you thinking of growing your own tomatoes at home, but don’t have a lot of space? Growing tomatoes in pots is a great solution for those with limited outdoor space or for those who want to bring the garden to their balcony or patio. I personally have had great success growing tomatoes in pots and I’d love to share my tips and tricks with you.
One of the biggest benefits of growing tomatoes in pots is the ability to control the soil and environment. You can choose the best potting mix and add fertilizer as needed to ensure that your plants have the proper nutrients to grow strong and healthy. Additionally, by keeping the plants in pots, you can easily move them around to find the sunniest spot in your home.
Another great thing about growing tomatoes in pots is that it’s easy to control pests and diseases. By keeping an eye on your plants, you can quickly spot any issues and take action before they become a bigger problem. Plus, it’s much easier to keep an eye on your plants when they are in pots, rather than trying to spot issues among a larger garden.
When it comes to choosing the right type of tomato to grow in pots, determinate varieties are a great choice. These varieties have a more compact growth habit and are less likely to become too large for your pots. Some examples of determinate varieties include ‘Patio’ and ‘Roma’.
When it comes to pot size, it’s important to choose pots that are at least 12 inches deep and 18 inches wide. This will give your plants enough room to grow and develop a strong root system. Additionally, be sure to choose pots with drainage holes to ensure that your plants do not become waterlogged.
So, go ahead and give it a try! Growing tomatoes in pots is a great way to enjoy fresh, homegrown tomatoes even if you don’t have a lot of outdoor space. Happy gardening!
Pot or container selection
When it comes to choosing the right type of pot to grow tomatoes from seeds at home, it’s important to consider a few key factors. The size and capacity of the pot, as well as the construction, all play a role in the growth and development of your plants.
First, let’s talk about size. To give your plants enough room to grow and develop a strong root system, it’s important to choose pots that are at least 12 inches deep and 18 inches wide. This will provide enough space for the roots to spread out and absorb the necessary nutrients for growth.
The capacity of the pot is also important. A pot that is too small will not be able to hold enough soil to support the growth of the plant. On the other hand, a pot that is too large may not be able to provide the warmth and moisture that the plant needs. A 5-gallon pot is a good option for growing tomatoes as it provides enough space for the plant while also being easy to move around if need be.
The construction of the pot is also important. It’s important to choose a pot that is made of a durable and non-toxic material, such as plastic or terra cotta. Additionally, be sure to choose pots with drainage holes to ensure that your plants do not become waterlogged. The drainage holes allow excess water to escape, preventing root rot and other issues caused by over-watering.
In summary, when choosing a pot to grow tomatoes from seeds at home, it’s important to consider the size and capacity of the pot, as well as the construction. A pot that is at least 12 inches deep and 18 inches wide, with a capacity of 5 gallons and made of durable and non-toxic material with drainage holes is a good option for optimal growth.
Make suitable soil mix
When it comes to growing tomatoes from seeds at home, the type and mixture of soil you use can have a big impact on the growth and development of your plants.
First, it’s important to use a high-quality potting mix specifically formulated for tomatoes. This type of mix contains the proper balance of nutrients and drainage that tomatoes need to thrive. A good potting mix will be a blend of peat moss, vermiculite, perlite, and compost or well-rotted manure.
In addition to a high-quality potting mix, it’s also important to ensure that your soil has the correct pH level. Tomatoes prefer a slightly acidic soil with a pH between 6.0 and 6.8. If your soil is too alkaline, you can add sulfur to lower the pH. If your soil is too acidic, you can add lime to raise the pH.
Another important factor to consider when it comes to soil mix is drainage. Tomatoes need well-draining soil to prevent root rot and other issues caused by over-watering. Be sure to add a layer of coarse grit, such as perlite or coarse sand, to the bottom of your pot before adding soil. This will help to improve drainage and keep your plants healthy.
In summary, when growing tomatoes from seeds at home, it’s essential to use a high-quality potting mix specifically formulated for tomatoes, with the correct pH level between 6.0 to 6.8, and proper drainage to promote optimal growth. Drainage can be improved by adding coarse grit to the bottom of the pot before adding soil.
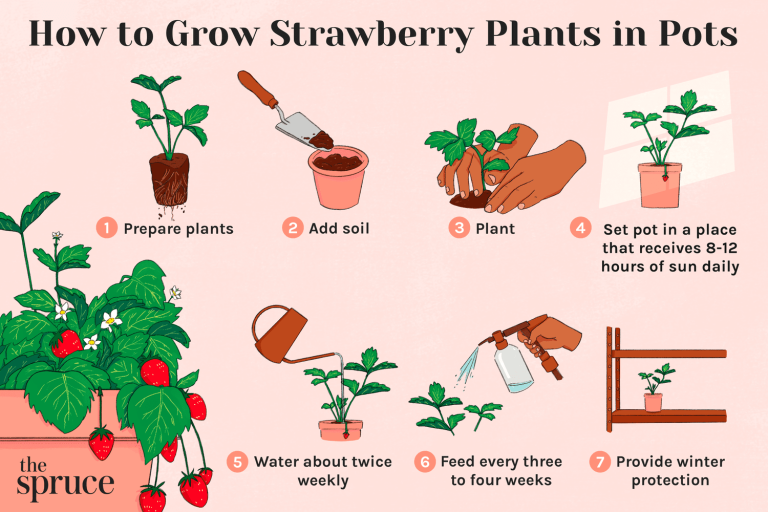
How to plant the tomatoes from seeds?
Step 1: Choose the right container
Choose a container that is at least 6 inches deep and has drainage holes at the bottom. You can use a plastic or clay pot, or even a container made from recycled materials such as a milk carton or a plastic container.
Step 2: Fill the container with soil
Fill the container with a high-quality potting soil that is specifically formulated for tomatoes. If you are using a container without drainage holes, add a layer of gravel or rocks to the bottom to improve drainage.
Step 3: Plant the seeds
Plant the tomato seeds about ¼ inch deep in the soil, spacing them about 2 inches apart. Cover the seeds with soil and press down gently to make sure they are in contact with the soil.
Step 4: Water the seeds
Water the seeds gently, making sure not to disturb the soil or the seeds. Keep the soil moist, but not waterlogged.
Step 5: Place the container in a warm location
Place the container in a warm location, such as a windowsill or a sunny spot in your house. Tomato seeds need a temperature of at least 70 degrees Fahrenheit to germinate.
Step 6: Wait for the seeds to germinate
Keep the soil moist and wait for the seeds to germinate, which can take anywhere from 5 to 10 days. Once the seedlings are about 2 inches tall, you can thin them out to leave only the strongest seedling in the pot.
Step 7: Transplant seedlings to a larger pot or outdoor
Once the seedlings are about 2 inches tall, you can transplant them to a larger pot or outdoor in the garden. Be sure to harden off the seedlings by gradually exposing them to outdoor conditions before transplanting them permanently.
Step 8: Water and fertilize regularly
Water the seedlings regularly and fertilize them every 2 weeks with a balanced fertilizer to promote healthy growth. Tomatoes need at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day to grow well.
Step 9: Harvest and enjoy!
Once the tomatoes are fully ripe, harvest them and enjoy! With proper care, your homegrown tomatoes should be ripe and ready to harvest in about 60-80 days.
How to care for tomatoes from seeds?
Watering Requirement
Tomatoes require consistent moisture to grow and produce fruit. The soil should be kept consistently moist, but not waterlogged. Overwatering can lead to issues such as root rot and fungal diseases. A good rule of thumb is to wait until the top inch of soil feels dry before watering again.
Fertilizer Requirement
Tomatoes require regular fertilization to promote healthy growth and fruit production. A balanced fertilizer, such as a 10-10-10 or 20-20-20, can be applied every 2-3 weeks. It is important to follow the recommended application rates on the fertilizer package. Over fertilization can lead to excess leaf growth and reduced fruit production.
Sunlight Needs
Tomatoes require at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day to grow well. A south-facing windowsill or a sunny spot in your house is ideal. If you don’t have a suitable location indoors, you can place the container outside during the warmer months, but be sure to bring it inside if temperatures drop below 50 degrees Fahrenheit.
Pruning & Training
Pruning and training the tomato plant can help to promote healthy growth and increase fruit production.
- Remove any suckers, or shoots that grow in the crook of the stem and the branches, as soon as they appear.
- Remove any yellow or dying leaves to improve air circulation and reduce the risk of fungal diseases.
- Stake or cage the plant to support the stem and branches as the plant grows and the fruit develops.
Other Care
Other care that may be necessary for growing tomatoes in a pot include:
- Monitoring for pests and diseases and taking appropriate action if necessary.
- Hardening off seedlings by gradually exposing them to outdoor conditions before transplanting them permanently, if planning to transplant them outdoors.
- Providing proper support to the plant as it grows and the fruit develops. This can be done by staking or caging the plant to prevent it from falling over.
Overall, tomatoes are relatively easy to grow in pots and with proper care, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of juicy, flavorful tomatoes.
Common problems
Pests
Tomato plants can be susceptible to a variety of pests, including aphids, whiteflies, and tomato hornworms. Aphids can cause damage to the leaves and stems of the plant, while whiteflies can weaken the plant by feeding on its sap. Tomato hornworms can consume large portions of leaves and fruit, potentially causing significant damage to the plant.
Diseases
Tomato plants can also be affected by a number of diseases, such as early blight, late blight, and septoria leaf spot. Early and late blight can cause leaf and fruit discoloration, wilting, and defoliation. Septoria leaf spot can cause brown or black spots on the leaves and can also lead to leaf loss. These diseases can be caused by a combination of environmental factors and improper care, such as overcrowding, poor drainage, and high humidity.
Poor Production
Poor production can also occur due to a number of issues, such as lack of sunlight, incorrect watering, and poor soil quality. Tomatoes need a lot of sunlight to produce fruit, so make sure the plants receive at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day. Overwatering or underwatering the plants can also cause poor production. It is important to monitor soil moisture and to not let the soil dry out or become waterlogged. Using poor quality soil or soil that does not have the proper balance of nutrients can also lead to poor production.
Other issues
Other common problems that tomato plants can face include:
- Cracking fruit: Tomatoes that are overripe or exposed to sudden changes in temperature can crack.
- Blossom end rot: This is caused by a calcium deficiency in the plant, and can be caused by uneven watering or a lack of calcium in the soil.
- Leggy plants: This can happen when the plants are not getting enough sunlight, or when they are planted too early in the season.
Harvesting & storing homegrown tomatoes from seeds
When to plant
Tomatoes can be planted from seed indoors 6-8 weeks before the last frost date in your area. They should then be transplanted into a sunny location with well-drained soil after all danger of frost has passed.
How to plant
- Fill seed trays or pots with seed compost and water well.
- Sow seed on the surface, following the packet instructions for spacing.
- Cover with a layer of compost or vermiculite.
- Place in a propagator or cover with a plastic bag and place in a warm place (minimum temperature of 15C/60F).
- Keep the compost moist but not waterlogged.
- When large enough to handle, transplant seedlings into 7.5cm (3in) pots.
- Gradually acclimatise to outdoor conditions for 10-15 days before planting out after all risk of frost, 45cm (18in) apart in a sunny spot in well-drained soil.
Harvesting
- Tomatoes are ready for harvesting when they are fully ripe and have a deep red color.
- You can also check for maturity by gently squeezing the fruit; if it gives slightly, it is ready to be picked.
- Tomatoes should be picked by the stem, leaving the calyx (the small green leafy part at the top) on the fruit.
Storing
- Tomatoes can be stored at room temperature, out of direct sunlight, until they are fully ripe.
- Once ripe, tomatoes can be stored in the refrigerator for up to a week.
- Tomatoes can also be frozen whole or as puree, diced or sliced for later use in cooking.
Note: Please keep in mind the above steps are general guidelines and the specific instructions for your area can vary depending on the climate, weather and soil conditions. Always consult a gardening guide or professional for advice on growing tomatoes in your area
Growing tomatoes from seeds in container – Conclusion
Conclusion
Growing tomatoes from seeds in a pot is a fun and rewarding way to enjoy fresh, homegrown vegetables. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can successfully grow healthy and productive tomato plants in a pot.
- Starting tomatoes from seed indoors, 6-8 weeks before the last frost date in your area.
- Planting seedlings in a sunny location with well-drained soil after all danger of frost has passed.
- Harvesting tomatoes when they are fully ripe and have a deep red color.
- Storing tomatoes at room temperature until they are fully ripe and keeping in the refrigerator for up to a week.
With a little bit of care and attention, you can grow delicious tomatoes in a pot and enjoy the taste of fresh, homegrown vegetables all season long.
It’s a great way to enjoy fresh produce and to have control over the quality of the food you are consuming. It’s also a great way to teach children about gardening, responsibility and healthy eating. So, give it a try, and you’ll be surprised by the results!