how to grow strawberries in a pot – [Beginners Guide]
Are you craving fresh and juicy strawberries but don’t have the space for a garden? Growing strawberries in a pot is the perfect solution! Not only is it a great way to enjoy your own homegrown strawberries, but it’s also a fun and easy way to get started with growing your own produce at home.
As someone who has tried growing strawberries in pots myself, I can tell you from personal experience that it’s a great way to enjoy fresh strawberries even in a small space. With a little bit of care and attention, you can have a thriving pot of strawberries in no time.
In this guide, we’ll go over everything you need to know to successfully grow strawberries in a pot, from choosing the right variety to planting, watering, and caring for your strawberries. We’ll also discuss some common problems and how to troubleshoot them.
So, are you ready to give it a go? Let’s dive into growing delicious strawberries in a pot!
Pot or container selection
When it comes to growing strawberries at home, choosing the right pot is key to the success of your plants. Here are some things to consider when selecting a pot for your strawberries:
Size and capacity
While strawberries are relatively small plants, they do require a certain amount of space to grow and produce fruit. Aim for a pot that is at least 12 inches (30 cm) in diameter and 12 inches (30 cm) deep. This size is suitable for a few plants and will allow them enough room to spread their roots and grow well.
If you have limited space, you can opt for a smaller pot, but be aware that your plants may not produce as much fruit as they would in a larger pot.
Construction
The construction of your pot is also important for the health of your strawberries. Here are some things to consider:
- Material: Opt for a pot that is made of a durable material, such as ceramic, plastic, or fiberglass. Avoid pots made of metal or wood, as they can leach chemicals into the soil or rot over time.
- Drainage: Ensure that your pot has drainage holes in the bottom to allow excess water to drain out. If your pot doesn’t have drainage holes, you can drill some yourself or add a layer of rocks or gravel in the bottom to improve drainage.
- Style: You can choose a pot with a decorative design or a more functional style, depending on your preference. Just make sure it’s well-suited for growing strawberries.
By choosing the right size and construction for your pot, you’ll set your strawberries up for success.
Make suitable soil mix
When it comes to growing strawberries in pots, having the right soil mix is crucial for their growth and development. Here are some things to consider when selecting soil for your strawberries:
Type
Use a high-quality potting mix specifically formulated for strawberries. This soil should be well-draining, fertile, and have a slightly acidic pH between 5.5 to 6.5. You can also add compost to the soil to improve its structure and fertility.
Mixture
A good soil mix for strawberries should be a combination of potting soil, compost, and perlite or vermiculite. This mixture will help provide good drainage, retain moisture, and provide adequate nutrients for your plants.
Additionally, you can also add organic fertilizers to the soil, such as well-rotted cow manure or chicken manure, to give your strawberries a boost.
By choosing the right soil mix and adding the right amendments, you can create the ideal growing environment for your strawberries and increase their chances of thriving in a pot.
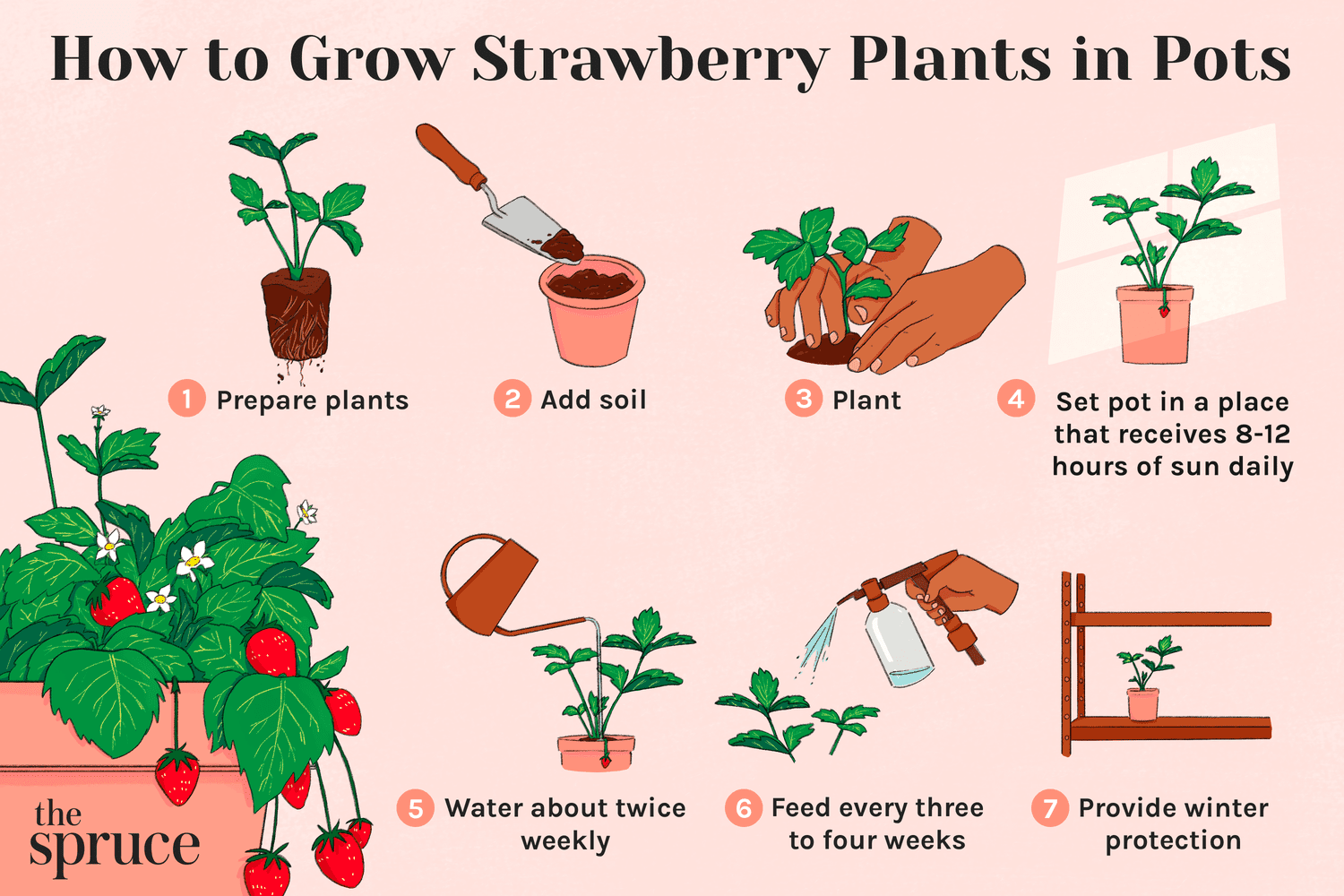
How to plant the strawberries?
Planting strawberries in pots is a great way to grow your own strawberries at home. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
Step 1: Choose the right pot
Select a pot that is large enough to accommodate the root system of your strawberry plant. A pot with a diameter of at least 12 inches and a depth of at least 8 inches is a good size for most strawberry varieties.
Make sure the pot has drainage holes to allow excess water to drain away from the roots. If the pot doesn’t have drainage holes, be sure to add some to the bottom before planting.
Step 2: Fill the pot with soil
Fill the pot with a well-draining potting mix. It’s important to have good drainage for strawberries to avoid root rot.
Step 3: Plant the strawberries
Remove the strawberries from their container, taking care to gently loosen the roots. Place the plants in the pot, making sure that the roots are covered with soil and the crown (where the leaves meet the roots) is level with the soil surface.
Space the plants about 12 inches apart, with room for growth. Water the plants well after planting.
Step 4: Provide support
Strawberries grow runners that develop into new plants. To keep them from becoming too crowded, you may want to provide a support system for the runners, such as a trellis or a ring of wire or plastic.
Step 5: Water and fertilize
Keep the soil moist, but be careful not to overwater. A good rule of thumb is to water the soil deeply once or twice a week, depending on the weather and the size of the pot.
As the plant grows, you may want to fertilize it with a balanced fertilizer. Strawberries prefer a slightly acidic soil with a pH between 5.5 and 6.5.
With a little care and attention, your strawberry plants will reward you with a bountiful harvest of sweet, juicy strawberries.
How to care for strawberries?
Watering Requirement
To care for strawberries in a pot, water deeply once or twice a week, depending on weather and soil conditions. Check soil moisture by sticking your finger about an inch into the soil. If it feels dry, it’s time to water. Avoid overwatering, which can cause root rot.
Fertilizer Requirement
Strawberries in a pot are heavy feeders and will benefit from a steady supply of nutrients. Use a balanced fertilizer, such as a 10-10-10 formula, according to package directions. Alternatively, use a slow-release fertilizer or compost. Avoid overfertilizing, which can lead to excessive foliage growth at the expense of fruit production.
Sunlight Needs
Strawberries need at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day. Place your pot in a sunny spot outdoors or indoors using a grow light.
Pruning & Training
Remove any yellow or diseased leaves and dead runners. Train your strawberries by using a trellis to support the plants as they grow. Pinch off any flowers that appear early in the season to promote root growth.
Other Care
Mulch the soil around the plants to retain moisture and suppress weeds. Protect from pests and diseases by checking for issues regularly. Common problems include aphids, spider mites, slugs, and root rot. Take action immediately to prevent them from spreading.
Common problems
Common problems that strawberries grown in a pot at home may face include:
Pests
Strawberries are susceptible to pests such as spider mites, aphids, and slugs. These pests can cause damage to the leaves and fruit of the plant. To prevent pests, try using natural methods such as introducing beneficial insects, such as ladybugs, or applying organic pest control solutions.
Diseases
Strawberries are also prone to diseases such as verticillium wilt, powdery mildew, and gray mold. These diseases can cause leaf and fruit damage, and can be spread through infected soil or water. To prevent diseases, it’s important to practice good hygiene by cleaning up fallen leaves and fruit, avoiding overhead watering, and using disease-resistant varieties of strawberries.
Poor Production
Strawberries grown in pots may also experience poor production due to various factors such as insufficient sunlight, improper watering, or lack of nutrients. To ensure good production, it’s important to provide your plants with the right amount of sunlight, water them regularly (but don’t overdo it), and fertilize them with a balanced fertilizer according to the package instructions. Additionally, overcrowding of plants and failure to remove runners can lead to reduced production.
Harvesting & storing homegrown strawberries
When harvesting homegrown strawberries, it’s important to wait until they are fully ripe to get the best flavor and texture. Ripe strawberries will be a deep red color and should be firm but slightly give when gently squeezed. You can also tell they are ripe when the fruit detaches easily from the plant. It’s best to harvest in the morning when the fruit is cool and to use a pair of scissors to snip the stem just above the fruit. Store the strawberries in the refrigerator immediately after harvesting, and avoid washing until you are ready to use them. For longer-term storage, you can freeze strawberries by washing and drying them, removing the stem, and placing them on a baking sheet to freeze until solid. Transfer the frozen strawberries to a resealable bag and store them in the freezer for up to 6 months.
Growing strawberries in container – Conclusion
Congratulations on learning how to grow strawberries in a pot! With the information presented, you are now equipped with the knowledge to grow your own fresh and delicious strawberries in the comfort of your home. By selecting the right pot, soil mix, and properly caring for your plants, you can enjoy the sweet taste of homegrown strawberries in a variety of recipes or simply as a healthy snack. So why not give it a try? With a little patience, effort, and care, you can have a successful harvest of your very own strawberries. We encourage you to get started on this exciting and rewarding adventure in gardening. Happy growing!