how to grow blueberries in a pot – [Beginners Guide]
Have you ever considered growing blueberries at home but don’t have a lot of space? Well, you’re in luck because growing blueberries in a pot is not only possible but also a great idea. Not only do blueberries offer numerous health benefits, but they also make for a beautiful and fruitful addition to your home garden.
As someone who has grown blueberries in pots for several years, I can vouch for the convenience and joy of having fresh blueberries right at my doorstep. Plus, growing blueberries in pots allows you to control the soil and growing conditions, making it easier to prevent common problems such as pests and diseases.
In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about growing blueberries in a pot, from selecting the right container and soil to pruning and harvesting your blueberries. We’ll also cover some tips and tricks to help you troubleshoot any issues that may arise along the way.
So, let’s get ready to plant some blueberries and enjoy the sweet rewards of home-grown fruit!
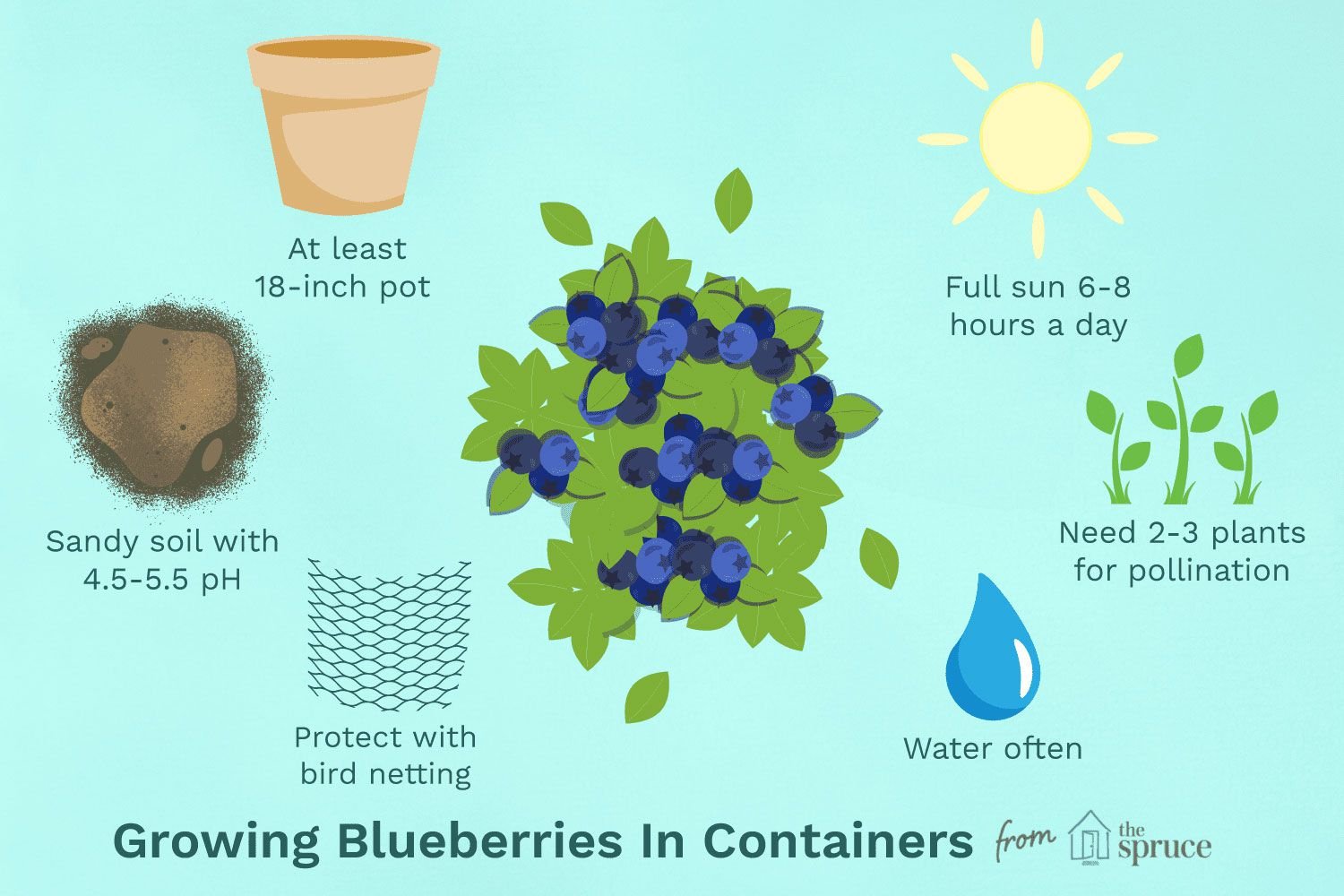
Pot or container selection
To grow blueberries at home, it’s recommended to use a pot that is at least 18 inches (45 cm) in diameter and 20 inches (50 cm) deep. The pot should also have good drainage holes and be made of a durable material like ceramic, plastic, or fiberglass. Additionally, it’s recommended to use an acidic soil mix with a pH of 4.5 to 5.5 and to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged.
Make suitable soil mix
When it comes to growing blueberries at home, it’s important to use a soil mix that is acidic and well-draining. Blueberries prefer soil with a pH between 4.0 and 5.0, so it’s recommended to use an acid-loving plant mix that contains peat moss, pine bark, and perlite or vermiculite. You can also add some sulfur or aluminum sulfate to lower the pH of the soil if needed. It’s important to avoid using garden soil or topsoil as these types of soil are not well-suited for container-grown plants and may not have the right composition for optimal growth.
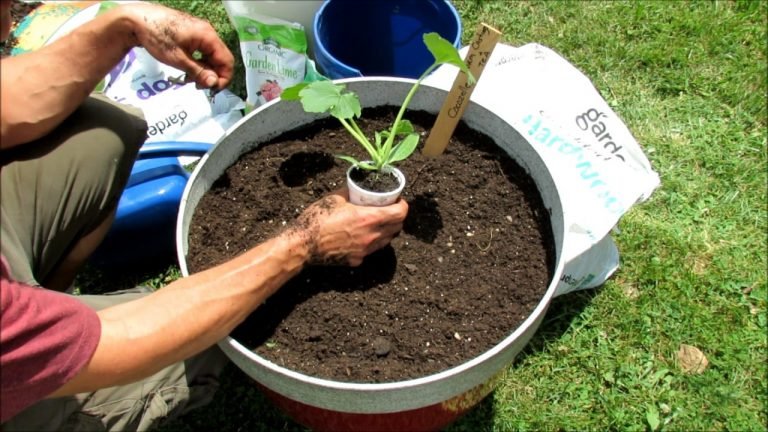
How to plant the blueberries?
Here is a step-by-step guide to planting blueberries in a pot at home:
Choose the right pot: Select a pot that is at least 16 inches in diameter and 18 inches deep. Make sure it has drainage holes to allow excess water to drain away from the roots.
Prepare the soil: Fill the pot with a soil mix that is specifically formulated for blueberries. This mix should have a pH between 4.5 and 5.5, as blueberries prefer acidic soil. You can also add some organic matter, such as peat moss or compost, to improve the soil quality.
Plant the blueberry bush: Remove the blueberry bush from its container and loosen the roots gently. Place the bush in the center of the pot, making sure that the root ball is level with the soil surface. Fill in around the root ball with soil and water it well to help settle the soil around the roots.
Mulch the soil: Add a layer of mulch around the base of the blueberry bush. This will help to retain moisture in the soil and keep the roots cool.
Water the plant: Water the blueberry bush deeply once or twice a week, depending on the weather and the size of the pot. Blueberries prefer moist, well-draining soil.
Fertilize the plant: Fertilize the blueberry bush with a fertilizer that is specifically formulated for acid-loving plants. Follow the instructions on the fertilizer package for the recommended amount and frequency.
Prune the bush: Prune the blueberry bush in late winter or early spring to remove any dead, damaged or diseased wood. This will help to promote new growth and ensure a healthy harvest.
By following these steps, you can successfully grow blueberries in a pot at home. Remember to give your blueberry bush plenty of sunlight, keep the soil moist, and fertilize it regularly to ensure optimal growth and a bountiful harvest.
How to care for blueberries?
Here is a step-by-step guide to planting blueberries in a pot at home:
Choose the right pot: Select a pot that is at least 16 inches in diameter and 18 inches deep. Make sure it has drainage holes to allow excess water to drain away from the roots.
Prepare the soil: Fill the pot with a soil mix that is specifically formulated for blueberries. This mix should have a pH between 4.5 and 5.5, as blueberries prefer acidic soil. You can also add some organic matter, such as peat moss or compost, to improve the soil quality.
Plant the blueberry bush: Remove the blueberry bush from its container and loosen the roots gently. Place the bush in the center of the pot, making sure that the root ball is level with the soil surface. Fill in around the root ball with soil and water it well to help settle the soil around the roots.
Mulch the soil: Add a layer of mulch around the base of the blueberry bush. This will help to retain moisture in the soil and keep the roots cool.
Water the plant: Water the blueberry bush deeply once or twice a week, depending on the weather and the size of the pot. Blueberries prefer moist, well-draining soil.
Fertilize the plant: Fertilize the blueberry bush with a fertilizer that is specifically formulated for acid-loving plants. Follow the instructions on the fertilizer package for the recommended amount and frequency.
Prune the bush: Prune the blueberry bush in late winter or early spring to remove any dead, damaged or diseased wood. This will help to promote new growth and ensure a healthy harvest.
By following these steps, you can successfully grow blueberries in a pot at home. Remember to give your blueberry bush plenty of sunlight, keep the soil moist, and fertilize it regularly to ensure optimal growth and a bountiful harvest.
Common problems
Growing blueberries in a pot at home can also face some common problems, such as:
Pests and Diseases
Blueberries can be attacked by pests such as spider mites, aphids, and blueberry maggot. Diseases such as anthracnose, powdery mildew, and root rot can also affect blueberry plants. To prevent these issues, use insecticides or fungicides as needed and follow good gardening practices, such as avoiding overhead watering and practicing good hygiene.
Improper pH
Blueberries prefer acidic soil with a pH of around 4.0 to 5.5. If the pH is too high, the plant may struggle to absorb nutrients and experience stunted growth or yellowing leaves. To prevent this issue, test the soil pH regularly and adjust it as necessary by adding acidic amendments such as sulfur.
Insufficient Pollination
Blueberries require pollination to produce fruit. If they are grown indoors or in a sheltered area, natural pollinators such as bees may not be present. Hand-pollination can be done by gently shaking the plant or using a small brush to transfer pollen from flower to flower.
Overcrowding
Overcrowding of plants in a pot can lead to competition for resources and poor growth or production. To prevent this issue, make sure to use a large enough pot and only plant one or two blueberry bushes per pot.
By taking preventive measures and addressing issues promptly, you can ensure that your blueberry plants grow healthy and produce a bountiful harvest.
Harvesting & storing homegrown blueberries
Blueberries are ready for harvesting when they are fully ripe and have a deep, rich blue color. The berries should be firm to the touch and have a slight give when gently squeezed. It’s important to avoid harvesting blueberries that are still white or green, as these berries are not yet fully developed and will not be as sweet or flavorful.
The timing of blueberry harvesting will vary depending on the specific variety and growing conditions, but as a general rule of thumb, blueberries are usually ready for harvest in late summer. Be sure to check your plants regularly and harvest the berries as soon as they are ripe to encourage continued production.
To store blueberries, it’s important to keep them dry and cool. Avoid washing the berries until you are ready to use them, as this can cause them to spoil more quickly. Store them in the refrigerator in a container with a lid or wrapped in plastic wrap. If you have a large harvest and need to store some of the blueberries for later, you can freeze them. To freeze blueberries, wash and dry them, then spread them out on a baking sheet and freeze until solid. Transfer the frozen berries to a resealable bag and store them in the freezer for up to six months.
In summary, harvesting and storing homegrown blueberries is a simple process. Wait until the berries are fully ripe, pick them gently, and store them in a cool, dry place. With proper care, your blueberries will stay fresh and flavorful for several days to a week, and can even be frozen for later use. Enjoy the sweet taste of homegrown blueberries in your favorite recipes!
Growing blueberries in container – Conclusion
Congratulations on learning how to grow blueberries in a pot! With the right pot, soil, and care, you too can enjoy fresh, delicious blueberries right at home. Growing blueberries in a pot is a great option for those with limited space, and it’s a fun and rewarding hobby that can provide you with a bountiful harvest.
Remember to choose the right pot and soil mix for your blueberry plant, and to provide it with adequate water and sunlight. With proper care and attention, your blueberry plant will thrive and reward you with sweet, juicy berries.
So why not give it a try? Growing blueberries in a pot is a great way to enjoy the benefits of homegrown produce, and it’s a fun and fulfilling activity for all ages. We hope that this guide has been helpful in getting you started, and we wish you the best of luck with your blueberry growing endeavors. Happy gardening!